10 May The talent textbook: 4 ideas for giving better feedback
The talent textbook: 4 ideas for giving better feedback
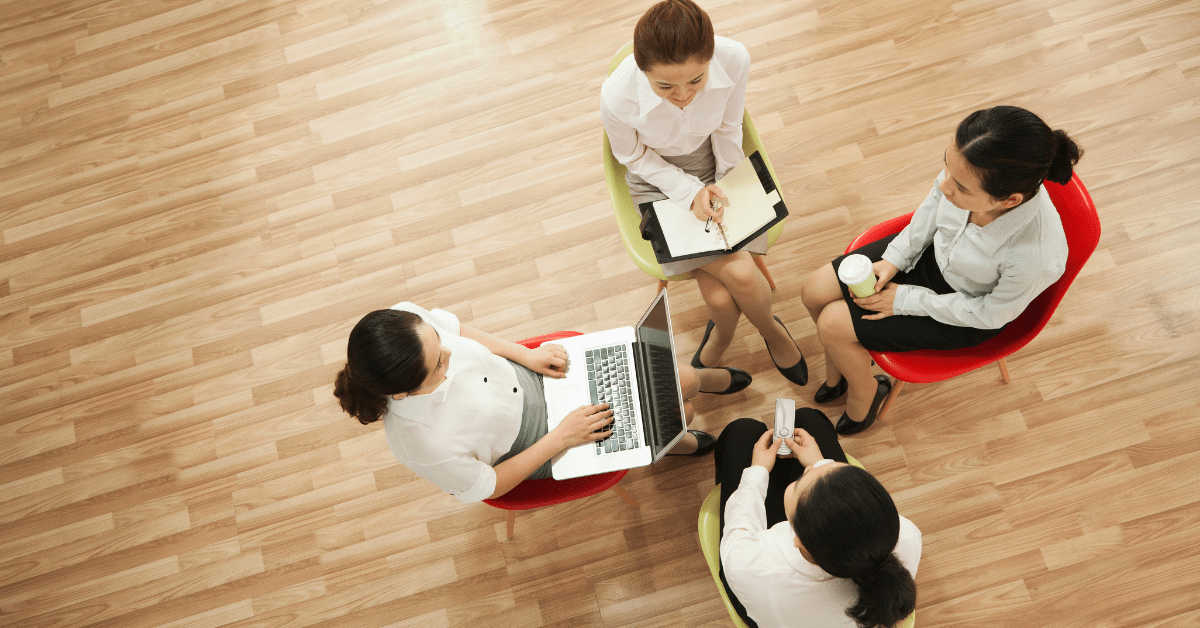
Coaching employees who need improvement, aren’t quite ready for higher pay, more responsibility, or leadership opportunities can be difficult. Continue reading this blog post from HR Drive for four ideas on giving better feedback.
“You got a promotion! You get a raise!” It’s almost as fun for managers to say it as it is for employees to hear. Giving good news during a review is easy, but how can reviewers take the sting out of constructive — or negative — feedback?
Coaching an employee who needs to improve or who isn’t quite ready for more responsibility, higher pay or leadership opportunities is perhaps the most difficult aspect of performance management, so in this installment of the Talent Textbook, we’ll offer four guiding principles from experts for giving better feedback.
#1: Meet more often
Many talent experts today recommend retiring the annual performance review and replacing it with frequent feedback instead. Unlike annual reviews, continuous feedback sessions can lessen anxiety for managers and workers both, making the conversations less formal and more focused. They can help send the message that the company culture is one of listening and responding to workers’ needs — and they help talent pros and managers minimize the risk that workers will be dissatisfied with or surprised by the discussion.
“That feedback should be coming constantly,” said Jim Flynn, CHRO at Sitel Group. “Everyone should know where they stand constantly.”
Flynn believes that frequency transforms the feedback session into a chance to reflect and recalibrate on priorities and goals. It can also ensure that workers are aware of their progress toward a pay increase, promotion or increased responsibility because their manager has reminded them more recently.
For Jodi Chavez, group president professional staffing group at Randstad Professionals, Randstad Life Sciences, focusing up frequently keeps managers better informed about workers’ desires and expectations, potentially preventing turnover and keeping the feedback session from devolving into a bidding war.
“If an employee has a desire and a belief that they want this promotion or to be in that role, there can be instances where you won’t be able to undo their desire to leave,” she said.
“It can be easier if you catch that earlier on in the process — so constant communication, so they know what you’re looking for and you can keep coaching them, is important. It only becomes an issue when no one knows that it’s a desire until later in the process.”
Just as you wouldn’t assess business goals and objectives only once a year, talent pros should expect to assess people often to curb employee disappointment, Flynn said, and this is especially true for employees early on in their careers.
#2: Give a heads up and an open ear
There’s still stress for talent pros and managers even when preparing to deliver feedback in a more casual session: Will they feel insulted? Will they disengage afterwards? The fears are relevant, so that’s why the way reviewers deliver feedback matters as much as the frequency.
Chavez and Flynn agree that managers and talent pros should begin conversations with what they’re going to cover in the session. They can continue to be transparent with workers by providing the reasoning behind the feedback and their expectations for the future, Flynn said.
“I think the old sandwich approach, employees see through that,” Flynn said, referring to the tactic of “sandwiching” a criticism between two compliments. “I would rather be more upfront and honest, and that should be the manager’s approach to everything.”
In that same realm, honest feedback should never come with bias or malice attached. Jeannie Donovan, VP of HR at Velocity Global, wrote in an email to HR Dive that “clear is kind” when it comes to constructive feedback. Whether the manager is discussing goal setting or areas that need improvement, the employee’s pay grade or their potential for a future promotion, Chavez said the same principle applies: stick to the facts and strive for objectivity.
“For new talent managers, I think it’s important to stay very factual and to hear the employee,” she said. “Don’t lead with false promises, just very cut and dried — ‘The role that you’re in and the experience that you have puts you at this level [of pay.]'”
That’s not to say that a manager should shut down further discussion, Chavez said. Discussing an employee’s strengths and listening to their desires can help them visualize a realistic and reachable future for themselves within the organization.
“It’s really important to sit down and talk about the positive things that the employee brings to the table — it’s a non-defensive position to put the employee in,” Chavez said. “Try to understand what is important to them, and let them tell you. ‘I may not be able to be a supervisor, but I’d still like to learn more about how to manage people’ — once you know that as a manager, giving them pieces that help fulfill that helps them stay engaged.”
#3: Support your managers
Talent pros should focus on workers when they consider their feedback best practices — but managers need their attention and expertise, too. As Flynn put it, “sometimes you have to carry cold water warmly” when delivering feedback, and managers need encouragement, support and guidance from talent pros to pull it off.
“A good HR business partner should understand when those difficult conversations could be occurring,” he said, noting that this partnership goes both ways. “If a manager is aware that it might be a tough conversation, it’s always a good idea to give your HR business partner a heads up so they can be attuned.”
Providing tools or suggestions for approaching reviews can help managers to execute conversations with employees with clarity and mutual understanding. For example, Donovan coaches her managers on the “stoplight exercise,” which can be helpful when an employee is making a case for a promotion. She said that managers can take a pen to the job description for the role their charge would like to be promoted into — highlighting current responsibilities in green, responsibilities they have a slight grasp of in yellow and tasks they’ve never touched in red.
“This is a straightforward way to identify strengths, weaknesses, and gaps to assess readiness for that promotion. Further, if this exercise yields gaps, the results indicate where exactly to focus on growth,” she wrote.
Donovan echoed Flynn’s belief that managers and talent pros should partner in the feedback process, and that debriefing afterwards is as critical for retention as it is for employee satisfaction.
“Have that second set of eyes to be aware and look for signs of disengagement or other harmful behavior,” said Flynn. “Some managers are hands off, so if they’ve had that difficult conversation make sure you’re maintaining that personal connection and increasing your frequency of touch.”
#4. Shift the focus forward
The last thing constructive feedback should sound like is a lecture. Reviewers should reiterate that the feedback is in service of plan to get that employee a promotion, salary bump, conference excursion, a chance to lead an internal workshop or whatever the goal is in the future, Chavez said.
“They should feel positive about what they have contributed and what they can continue to contribute,” she said. “[It’s about] what you can do to help foster that growth for them.”
Flynn’s approach is similar, keeping the conversation productive and goal-oriented: “I probably spend 25% of the time talking about past performance, and goals reached and past behavior, but I like to focus more on what are the strengths, what are weaknesses and where the potential is.”
With the future in mind, Chavez points out that a transparent, frequent and collaborative review process could prevent promising talent from leaving down the road. It can even have ripple effects across an organization, according to Donovan, who saw that workers had a clearer vision of their goals when she transitioned to more continuous feedback.
“As a result of our laser-focus on more frequent performance conversations, our employees have a roadmap of what needs to be done and when, and this approach lends itself to higher productivity and a general sense of purpose across the board,” Donovan wrote.
SOURCE: Fecto, M. (10 April 2019) “The talent textbook: 4 ideas for giving better feedback” (Web Blog Post). Retrieved from https://www.hrdive.com/news/the-talent-textbook-4-ideas-for-giving-better-feedback/552276/